

- Create bootable usb from iso windows 7 command line how to#
- Create bootable usb from iso windows 7 command line install#
- Create bootable usb from iso windows 7 command line download#
Start the DiskPart utility by typing diskpart at a command prompt, and issue the following commands:. Insert the target USB Flash Drive into the computer.  You’ll need to use the DiskPart utility on the system you will use to prep the USB flash drive.
You’ll need to use the DiskPart utility on the system you will use to prep the USB flash drive. Create bootable usb from iso windows 7 command line how to#
How to Make a Bootable USB Flash Drive Without Using the bootsect Command:
All data on this USB flash drive will be lost!. This USB flash drive will be totally erased and formatted with NTFS!. A USB Flash Drive that has a capacity of 4GB or larger. You’ll still need your own valid product id key to activate Windows 7. Create bootable usb from iso windows 7 command line download#
You can download ISO’s from the list of Windows 7 ISO Direct Download Links. An ISO of the Windows 7 installation DVD or a Windows 7 disc. Using the Windows 7 USB/DVD Download Tool to Create a Bootable Windows 7 USB Flash Drive. How to Make a Bootable USB Flash Drive Without Using the bootsect Command:. For this very reason, I’ll try to explain the process as simply as possible. Through this and many other examples, I’ve recently become an advocate of preferring the command line over the UI, even for people who aren’t very familiar with terminal commands. I’m sure you’ve seen that it doesn’t require any additional application to be installed and it takes much less time than some UI applications. Of the many ways to create a bootable USB stick, we looked at the Terminal application for this purpose. The dd command starts writing the ISO file to your USB stick and displays a status bar.Īfter a few minutes, your bootable USB stick with the Ubuntu ISO on it is ready. I will be using the following command to write the Ubuntu ISO on my USB stick: $ sudo dd bs=4M if=/home/sana/Downloads/ubuntu-20.04.2-live-server-amd64.iso of=/dev/sdb1 status=progress oflag=sync Tip: Instead of typing the command, you can copy it from here and paste into the Terminal by using the Ctrl+Shift+V, or by using the Paste option from the right-click menu. $ sudo dd bs=4M if=/path/to/ISOfile of=/dev/sdx status=progress oflag=sync This is the dd command syntax you can use in your Terminal: Now that you have unmounted the USB, you know your ISO image’s name and path, and you know your device name, it takes only one command to create a bootable USB. You can also use the device name to unmount it: $ sudo umount /device/nameįor example, I would use the following device name to unmount the USB: $ sudo umount /dev/sdb1 Step 4: Create a bootable Ubuntu stick By using the path your USB is mounted on: $ sudo umount /path/where/mountedįor example, I would use the following path to unmount the USB: $ sudo umount /media/sana/'Ubuntu-Server 20.04.2 LTS amd64'Ģ. There are two ways you can unmount the USB from your Ubuntu:ġ. Note down the device name (/dev/sdb1 in my case) and the path it is mounted on (/media/sana/Ubuntu-Server 20.04.2 LTS amd64 in my case). The last line in the output of my df command lists the USB that is mounted to my Ubuntu system. Insert the USB into your system and then run the following command in order to fetch your USB’s name: $ df 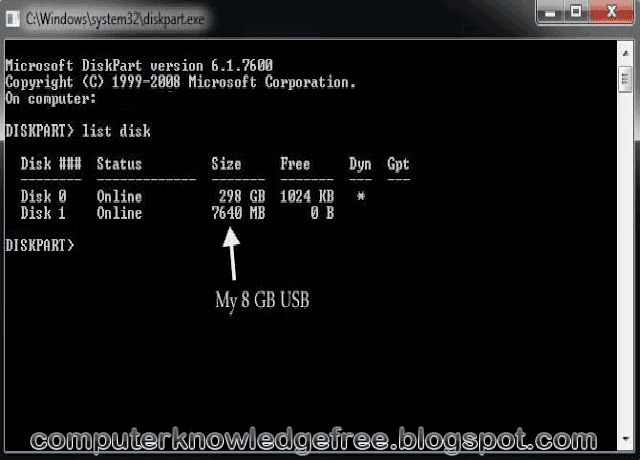
Open your Ubuntu command line, the Terminal, either through the Ubuntu Application Launcher search or by using the Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut.īefore you write your USB stick, you need to make sure that it is not automatically mounted to your Ubuntu. The direct download link at the time of writing this guide was: Step 2: Open Ubuntu Terminal iso package will be saved in your downloads folder. Select the Save file option and then click OK. This will open the dialog to save the file. I’ve been using the “ Download Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS” link under Ubuntu Server. Open the Official Ubuntu website through any installed web browser and download the Ubuntu ISO through the following download link:Ĭlick on any Ubuntu version you want to install. Please follow these steps in order to create a bootable Ubuntu USB from your terminal. We have run the commands and procedures mentioned in this article on an Ubuntu 20.04 LTS system. The command-line tools don’t consume too many resources, so they are a good alternative to the widely used graphical applications, especially if you can’t cope with older hardware. Using the terminal makes certain tasks more efficient and even faster. The terminal is a good alternative to doing your tasks through the Ubuntu user interface. In this article, we will use the Ubuntu command line, the terminal, to create a bootable Ubuntu USB stick. Some involve using the system tools, while others require external packages to be installed. There are many ways to create a bootable USB stick in Ubuntu.
You can use the USB stick to fix configuration problems with the standard tools that come with the Ubuntu ISO package. A different Ubuntu flavor can be run directly from a USB stick. Create bootable usb from iso windows 7 command line install#
You can use a bootable USB Stick to install or upgrade Ubuntu. Why do you need a bootable USB stick under Ubuntu? Here are some possible reasons:







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
